Apple Farming
Apple farming has emerged as one of the most lucrative agricultural ventures in recent years, offering farmers an excellent opportunity to generate substantial income. With the increasing demand for apples in both domestic and international markets, this fruit has become a high-value crop that promises impressive returns. However, the key to success lies in proper planning, effective management, and the adoption of modern farming techniques. By focusing on semi-dwarf apple cultivars like Gala, Golden delicious and Fuji, farmers can achieve higher yields per acre while optimizing space and resources.
Every aspect of apple farming profit will be covered in this blog post, including projected income, yearly maintenance expenditures, and initial investment prices. The financial and practical sides of apple farming will be thoroughly explained in this blog, regardless of your level of experience as a farmer or your desire to learn more about apple growing. Along with sharing planting and growing the best practices, we’ll make sure you have the resources and know-how necessary to optimize your earnings. After reading this article, you’ll know why growing apples is not only a conventional agricultural activity but also a lucrative commercial endeavor that has the ability to change your financial situation.
Pre-Planting Preparation for Apple Farming
Proper land preparation before planting apple saplings is essential to ensure healthy tree growth, better yields, and long-term orchard productivity. Preparing the planting site carefully provides the saplings with the ideal environment for root establishment and nutrient uptake. Below are the detailed steps to prepare the land effectively:
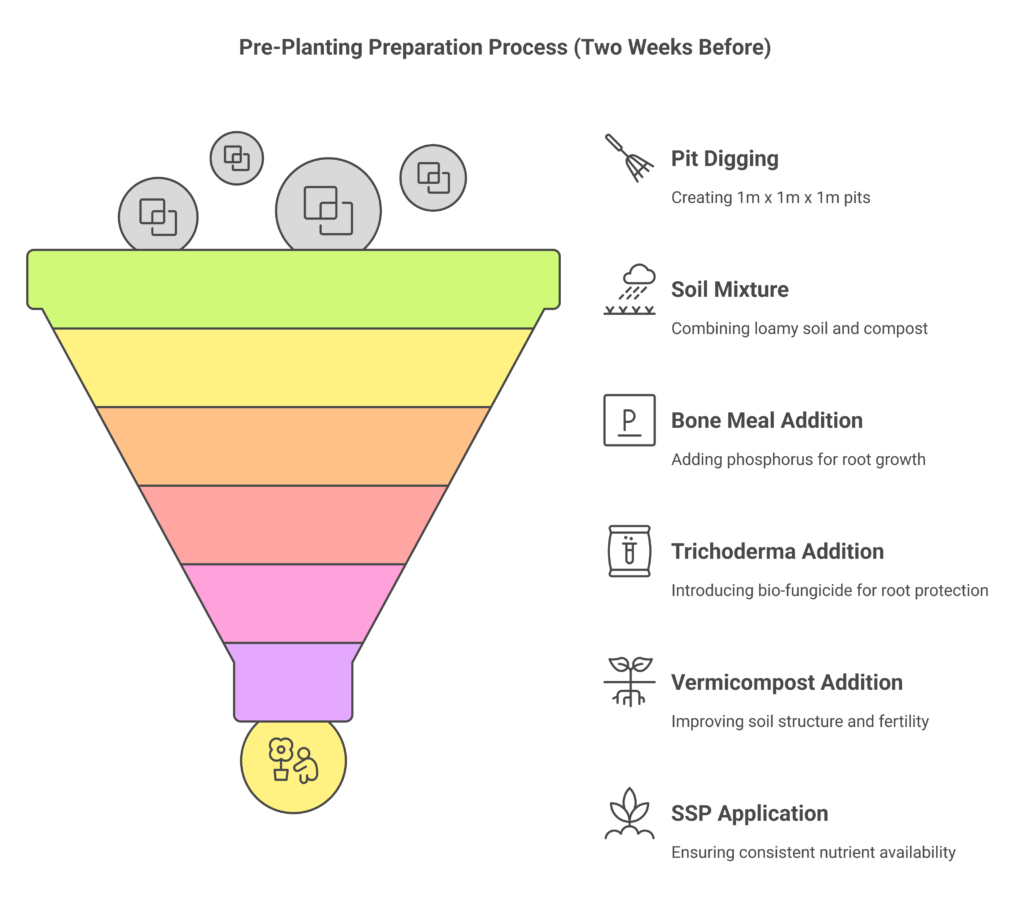
1. Pit Preparation
Preparing planting pits is a crucial step in establishing a healthy and productive orchard. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Pit Size and Timing: Dig pits measuring 1 meter in length, width, and depth (1m x 1m x 1m) at least two weeks before planting. This size ensures sufficient space for root expansion and proper aeration, which are vital for the tree’s growth.
- Soil Preparation: Fill the pits with a well-balanced mixture of loamy soil, organic compost, and biofertilizers. This enriched blend provides essential nutrients and promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms, creating an ideal environment for strong root development in the early stages.
2. Amendments for Each Pit
To boost soil fertility and provide the necessary nutrients for the healthy growth of young saplings, add the following inputs to each planting pit:
- Bone Meal (50g): A natural source of phosphorus, bone meal promotes strong root development and enhances the overall vigor of the plant.
- Trichoderma viridae (50g): This bio-fungicide protects the roots from harmful soil-borne pathogens while improving root health and resilience.
- Vermicompost (10 kg): An organic fertilizer that increases microbial activity, improves water retention, and improves soil structure. This promotes sustained growth and guarantees soil fertility over the long run.
- Single Super Phosphate (SSP) (60-100g): A phosphorus fertilizer that releases nutrients gradually and sustains constant root and shoot growth over time.
Planting Density
One of the most critical factors in apple farming is determining the optimal planting density. This ensures that each tree has enough space to grow, access to sunlight, and proper airflow, which are essential for healthy development and high yields. For semi-dwarf apple cultivars like Gala and Fuji, the recommended planting density is 253 plants per acre, with a spacing of 4 meters x 4 meters.
Tips for Planting and Layout
- Use a grid layout to ensure uniform spacing and ease of orchard management.
- For sloped terrains, align the rows along the contour lines to prevent soil erosion and improve water retention.
- Consider planting windbreaks around the orchard to protect young trees from wind stress, which can hamper growth and affect fruit set.
- Ensure consistent irrigation across the orchard to avoid competition between trees for water resources.
Cost of Investment per Acre for Apple Farming
All costs are provided in Nepalese currency (NRs.) and are approximate estimates. Actual costs and yields may vary depending on factors such as location, apple cultivar, and prevailing market conditions. It is recommended to consult local agricultural experts for personalized guidance and accurate planning.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the initial investment required for apple farming:
| S.N. | Categories | Estimated Cost (NRs.) |
| 1 | Land Preparation (plowing, leveling, pit digging) | 70,000 |
| 2 | Apple Saplings (253 plants * NRs. 300) | 75,900 |
| 3 | Fertilizers and Manure | 101,200 |
| 4 | Irrigation System Setup (Drip) | 200,000 |
| 5 | Labor Costs (Planting, Maintenance) | 70,000 |
| 6 | Pest & Disease Control | 40,000 |
| 7 | Miscellaneous Costs (Pesticides, Mulch, etc.) | 60,000 |
| Total Cost | 780,000 |
Also Read About: Lemon Farming Profit Per Acre
Annual Maintenance Costs for Apple Farming
Maintaining an apple orchard involves ongoing expenses to ensure healthy tree growth, high fruit quality, and maximum yields. From the second year onward, the annual maintenance costs typically range from NRs. 150,000 to 200,000 per acre, depending on the variety, orchard size, and local conditions. Below is a detailed breakdown of the key components of these costs:
- Fertilizers and Manure
- Fertilizers and organic manure are crucial to replenishing soil nutrients and promoting tree health.
- Regular application of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) fertilizers is required to support flowering, fruiting, and overall tree vigor.
- Organic options like vermicompost or farmyard manure (FYM) can be used to improve soil structure and microbial activity.
- Estimated Cost: NRs. 30,000–50,000 per acre annually.
- Pest and Disease Control
- Regular monitoring and management of pests (e.g., codling moth, aphids) and diseases (e.g., apple scab, powdery mildew) are essential.
- Expenses include insecticides, fungicides, and biological control agents to prevent yield losses.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM) practices can help reduce chemical use while maintaining effectiveness.
- Estimated Cost: NRs. 20,000–40,000 per acre annually.
- Labor Costs
- Labor is required for various activities such as:
- Pruning: Essential for shaping the tree, maintaining airflow, and promoting healthy fruiting.
- Weeding: Prevents competition for nutrients and keeps the orchard clean.
- Harvesting: Skilled labor ensures proper handling of fruit to avoid damage.
- Estimated Cost: NRs. 50,000–70,000 per acre annually.
- Irrigation
- Apple trees require consistent irrigation, especially during dry months and critical growth stages like flowering and fruit setting.
- Costs include water charges, maintenance of irrigation systems (e.g., drip or sprinkler systems), and electricity or fuel expenses for pumps.
- Estimated Cost: NRs. 20,000–30,000 per acre annually.
- Miscellaneous Expenses
- Additional costs may include:
- Replacement of damaged or unproductive trees.
- Purchase and maintenance of orchard tools and equipment.
- Soil testing and pH adjustments, if necessary.
- Estimated Cost: NRs. 10,000–20,000 per acre annually.
Estimated Income from 1 Acre Apple Farming
The income from apple farming increases significantly as the trees mature. Below is a year-wise breakdown of the estimated income:
| Year | Yield per Tree (Kg) | Yield per Acre (Kg) | Market Price (NRs/kg) | Total Income (NRs.) |
| 2nd Year | 10 | 2,530 | 100 | 253,000 |
| 3rd Year | 20 | 5,060 | 100 | 506,000 |
| 4th Year | 35 | 8,855 | 100 | 885,500 |
| 5th Year | 50 | 12,650 | 100 | 1,265,000 |
| 6th Year+ | 70 | 17,710 | 100 | 1,771,000 |
Apple Farming Profit Analysis
- Initial Investment: NRs. 780,000
The initial investment for apple farming includes all the upfront costs required to establish a productive orchard. This one-time expense of NRs. 780,000 per acre covers land preparation, purchasing saplings, fertilizers, irrigation setup, labor, and other miscellaneous costs. This investment is crucial for laying a strong foundation for healthy tree growth and high yields in the future.
2. Annual Maintenance: NRs. 150,000 – 200,000 (From the Second Year Onward)
Once the orchard is established, annual maintenance costs are incurred to ensure the trees remain healthy and productive. These recurring expenses, ranging from NRs. 150,000 to NRs. 200,000 per acre, including fertilizers, pest and disease control, labor for pruning and harvesting, irrigation maintenance, and other miscellaneous costs. Proper maintenance is essential for sustaining the orchard’s productivity and maximizing yields.
3. Income: By the 5th Year
By the 5th year, the apple orchard reaches a stage of partial maturity, and the trees begin to produce substantial yields. With an estimated income of NRs. 1,265,000 per acre in the 5th year, the cumulative earnings from the 2nd to the 5th year are sufficient to recover the initial investment of NRs. 780,000. This marks a significant milestone in the profitability of the orchard.
4. Income: Net Profit of Over NRs. 1.5 million Annually
From the 6th year onward, the orchard reaches full maturity, and the trees produce their maximum yield. With an estimated annual income of NRs. 1,771,000 per acre and annual maintenance costs of NRs. 150,000 – 200,000, the net profit per acre exceeds NRs. 1.5 million annually. This high-income potential makes apple farming a highly lucrative and sustainable agricultural venture.
Key Tips for Success in Apple Farming
Achieving success in apple farming requires careful attention to several critical factors, from soil preparation to market awareness. Below are the key tips to ensure a thriving and profitable apple orchard:
- Soil and Climate Requirements
Apples thrive best in well-drained loamy soil with a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5. Conduct a soil test before planting to confirm the soil’s suitability and make necessary adjustments using lime or sulfur. Additionally, apples require a cold climate to ensure proper dormancy and flowering, which are essential for fruiting. Orchards should ideally be located in regions with distinct winter and summer seasons for optimal growth and yield.
- Efficient Irrigation Management
Using a drip irrigation system is highly recommended while growing apples. This method ensures efficient water use by delivering water straight to the root zone, reducing waste, and maintaining constant soil moisture levels. Another advantage of drip irrigation is fertilization, which facilitates fertilizer application. Appropriate irrigation is particularly crucial during flowering, fruit setting, and dry spells to prevent water stress and improve fruit quality.
- Pest and Disease Management
To detect and control diseases and pests that could endanger apple orchards, routine monitoring is crucial. Aphids, codling moths, powdery mildew, and apple scab are common problems. Use Integrated Pest Management (IPM) techniques to efficiently control pests while reducing the need for chemicals. To stop infections from spreading, use bio-fungicides like Trichoderma viridae and keep your orchard clean. Protecting yields requires early discovery and prompt action.
- Annual Pruning
Pruning is a crucial practice to enhance tree health and productivity. Prune trees annually to improve sunlight penetration and air circulation within the canopy. This reduces the risk of fungal diseases, encourages uniform fruit development, and improves fruit size and quality. Proper pruning also helps maintain tree shape and makes pest control and harvesting more efficient.
- Market Research and Planning
Stay updated on market prices and consumer demand to make informed decisions about harvesting and selling. Explore both local and export markets to maximize profits. Timing your harvest to align with peak demand periods can significantly enhance returns. Additionally, consider opportunities for value addition, such as processing apples into juice, cider, or dried products, to diversify income streams.
Conclusion
Apple farming is a highly profitable venture with proper planning and management. While the initial investment is significant, the returns from the 5th year onward make it a worthwhile endeavor. By following the best practices in planting, maintenance, and pest control, you can achieve a net profit of over NRs. 1.5 million per acre annually once the trees reach full maturity.



Pingback: Avocado Farming Profit Per Acre -