Jackfruit Farming
Jackfruit farming offers a profitable long-term agricultural opportunity, though it requires significant initial investment and patience. The first-year setup costs, including land preparation, saplings, irrigation, and labor, total approximately NRs. 298,900 per acre, with annual maintenance costs averaging NRs. 75,000 from the second year onward. While the first six years may result in losses due to low or no income, the orchard starts generating revenue from the third year, with yields increasing substantially by the seventh year.

From Year 7 to Year 20, farmers can achieve an annual net profit of NRs. 492,000, driven by high yields and favorable market prices. Over a 20-year lifespan, the cumulative jackfruit farming profit per acre can reach NRs. 6,806,300. This makes jackfruit farming a sustainable and lucrative venture for those willing to manage upfront costs and wait for the trees to mature. With proper planning and maintenance, jackfruit farming can deliver significant returns, making it an attractive option for long-term agricultural investment.
Land Preparation
Careful ground preparation is necessary to create the ideal growing environment for jackfruit. In order to guarantee adequate drainage, aeration, and consistent water distribution, the process starts by removing the area of rocks, debris, and weeds. A appropriate planting base is then created by plowing and leveling the soil.
The addition of organic matter, such manure or compost, improves microbial activity, soil fertility, and water retention—all of which are essential for the growth of healthy trees and higher yields. An essential first step in creating the conditions for a productive jackfruit plantation and strong plant growth is proper site preparation.
Soil Type
Jackfruit prefers deep, fertile soils that drain easily, like sandy loam or loam, with a pH between 6.0 and 7.5. Avoiding soggy or poorly drained soils is crucial because they can harm the development of the tree’s roots and overall health. This crop is adaptable to a range of conditions and can thrive in lowlands as well as at elevations of up to 1200 meters. Choosing the proper soil type is crucial to guaranteeing robust development and producing fruit of superior quality.
Climatic Requirements
Jackfruit is ideally suited to tropical and subtropical climates, where it thrives under specific environmental conditions. The tree prefers temperatures between 25°C and 35°C, which provide the warmth needed for robust growth and fruit development. Consistent temperatures within this range enhance photosynthesis, flowering, and fruiting.
Additionally, jackfruit requires an annual rainfall of 1,500 to 2,500 mm for optimal growth, as sufficient moisture is crucial for supporting its large leaves and fruit production. Once established, the tree demonstrates a degree of drought tolerance, allowing it to endure periods of water scarcity. This adaptability makes jackfruit a resilient crop in areas with fluctuating rainfall patterns. Warm temperatures and adequate rainfall are critical for maximizing the tree’s growth potential and ensuring high-quality fruit yields.
Major Cultivars
There are many different cultivars of jackfruit, including “Singapore Jack,” “Black Gold,” “Golden Pillow,” and “Honey Gold,” each of which has unique qualities like sweetness, size, and texture. To guarantee optimal output, exceptional fruit quality, and profitability, the choice of cultivar should be based on market demand and local climate circumstances. Selecting the right variety is essential to attaining agricultural and commercial success since it not only increases the likelihood of successful farming but also conforms to customer tastes.
Planting

| Aspect | Details |
| Planting Season | The ideal planting season for jackfruit is between June and October, coinciding with the rainy season in tropical and subtropical regions. This ensures adequate water supply for root development and early growth. |
| Spacing | Plant grafted saplings at a spacing of 8 x 8 meters. |
| Pit Preparation | Dig pits measuring 1m x 1m x 1m. Fill each pit with a mixture of topsoil, 10 kg of farmyard manure (FYM), and 1 kg of neem cake to enrich the soil and promote healthy root development. |
| Planting Method | Place the sapling in the center of the pit, ensuring the root ball is level with the soil surface. |
| Number of Plants per Acre | Approximately 63 plants can be planted per acre. |
Intercropping in Jackfruit Farming
Intercropping is a highly advantageous practice in jackfruit farming, particularly during the initial years when the trees are maturing and not yet yielding fruit. The space between jackfruit trees can be efficiently utilized by planting short-term crops, with the choice of intercrops varying according to the season:
a). Rainy Season (June–October)
During this period, crops like turmeric, ginger, and leafy greens (e.g., spinach or amaranth) thrive due to the abundant moisture. Legumes such as beans or peas can also be grown, as they fix nitrogen in the soil, improving fertility.
b). Winter Season (November–February)
Cool-season vegetables like tomatoes, peppers, and cabbage are ideal for intercropping. These crops benefit from moderate temperatures and require less water, reducing competition with jackfruit trees.
c). Summer Season (March–May)
Drought-tolerant crops such as cowpeas or short-duration vegetables like okra can be cultivated during this period. Mulching and proper irrigation management are essential to conserve soil moisture and minimize resource competition.
Intercropping not only maximizes land use but also provides farmers with additional income while waiting for the jackfruit trees to mature. It is crucial to select intercrops that do not heavily compete for nutrients, water, or sunlight. Proper planning and management of intercropping systems can enhance soil fertility, suppress weed growth, and boost overall farm productivity, making it a sustainable and profitable strategy for jackfruit cultivation.
Irrigation
The water requirements for jackfruit plants vary significantly depending on factors such as growth stage, climate, soil type, and environmental conditions. Below is a general overview of the water needs per jackfruit plant per day at different growth stages. It is important to note that these values are approximate and may vary based on specific conditions.
a). Planting to 1 Year
During the initial year, young jackfruit plants require consistent moisture to establish their root systems. The water requirement typically ranges between 5 to 10 liters per plant per day. Proper irrigation during this stage is crucial for healthy root development and early growth.
b). 1 to 3 Years
As the plants grow and develop, their water needs increase. During this stage, the water requirement ranges from 10 to 20 liters per plant per day. Adequate irrigation supports the plant’s transition from a sapling to a more established tree.
c). 3 to 5 Years
During this phase, the jackfruit plant matures and requires more water to support vegetative growth. The water requirement increases to 20 to 30 liters per plant per day. Consistent watering ensures the tree remains healthy and prepares it for future flowering and fruiting.
d). 5 Years and Above
Mature jackfruit trees have higher water demands, especially during flowering and fruiting stages. The water requirement ranges from 30 to 50 liters per plant per day. Proper irrigation during this stage is essential to maximize fruit yield and maintain tree health.
Understanding and meeting the water requirements at each growth stage is critical for the successful cultivation of jackfruit, ensuring optimal growth, development, and fruit production.
Fertilizer and Manure
The development stage, soil fertility, and environmental factors all affect how much fertilizer jackfruit plants need. The general requirements for manure and fertilizer per jackfruit plant at various growth stages are listed below. These figures are estimates that should be modified in light of particular growth circumstances and the findings of soil tests.
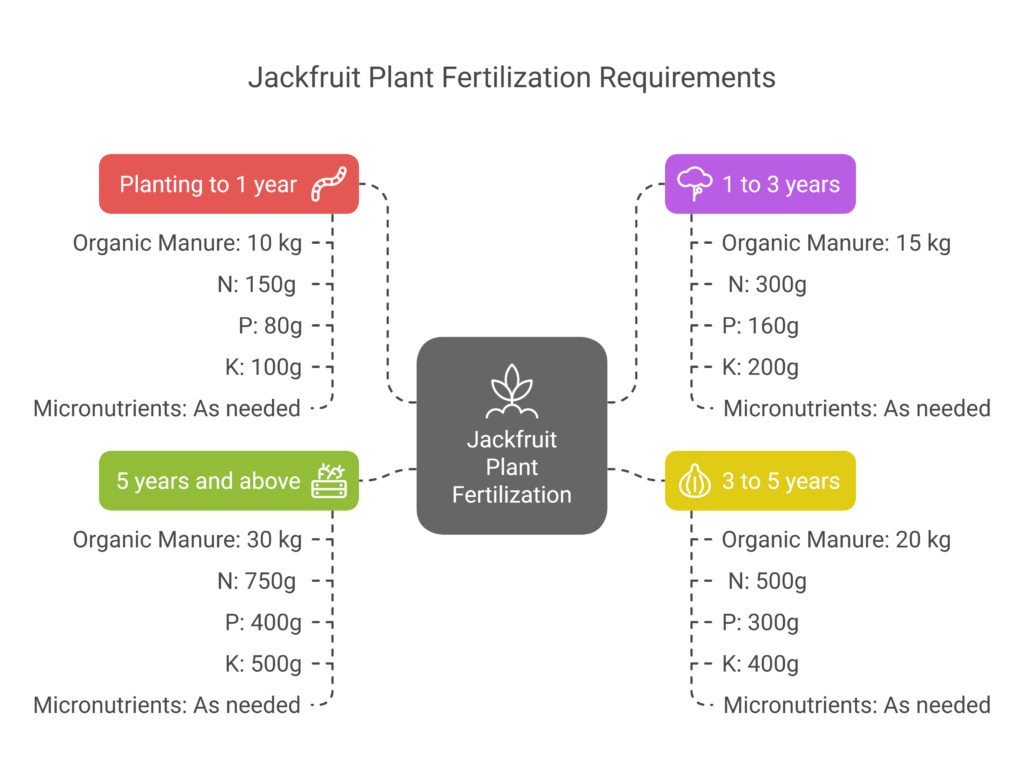
a). Planting to 1 Year
During the first year, the focus is on root development and plant establishment. Each plant requires approximately 10 kg of organic manure, along with 150g of nitrogen (N), 80g of phosphorus (P), and 100g of potassium (K) per year. Micronutrients should be applied as needed to support healthy growth.
b). 1 to 3 Years
In this stage, the goal is to promote vegetative growth and canopy development. The fertilizer requirement increases to 15 kg of organic manure, 300g of nitrogen, 160g of phosphorus, and 200g of potassium per plant annually. Micronutrients should be applied based on the plant’s needs.
c). 3 to 5 Years
As the plant matures and begins early fruiting, its nutrient demands grow. Each plant requires around 20 kg of organic manure, 500g of nitrogen, 300g of phosphorus, and 400g of potassium per year. Micronutrients should be applied as necessary to support continued growth and fruit development.
d). 5 Years and Above
At this stage, the focus shifts to maximizing fruit production and quality. Mature trees require approximately 30 kg of organic manure, 750g of nitrogen, 400g of phosphorus, and 500g of potassium per plant annually. Micronutrients should be applied as needed to ensure optimal fruit yield and tree health.
Proper fertilization and manure application, tailored to the plant’s growth stage, are essential for healthy jackfruit cultivation and high-quality fruit production.
Weed Control
Controlling weeds is crucial to ensuring that jackfruit trees receive enough sunlight, water, and nutrients, especially in the early phases of growth. Regular weeding and mulching around the tree’s base can result in effective weed management by preventing weed growth and preserving soil moisture. In order to reduce chemical interference, hand weeding is frequently preferable, even though herbicides can be used sparingly. It is strongly advised to use an integrated weed management strategy that incorporates techniques including hand weeding, intercropping, cover cropping, and the selective use of herbicides as needed. This all-encompassing approach encourages sustainable farming and helps jackfruit trees grow healthily.
Pest and Disease Management
Common pests
| Pest | Symptoms | Management |
| a). Brown Weevil | Damages fruits and buds by creating holes, tunnels, or feeding marks. Grubs and adults feed and reproduce inside, causing premature fruit drop and significant yield losses. | · Destroy fallen fruits and buds. · Collect and destroy grubs and adults. · Spray trees with monocrotophos (0.035%).
|
| b). Shoot and Fruit Borer | Bores into shoots and fruits, leading to wilting, fruit rot, premature fruit drop, and visible frass. | · Spray monocrotophos 36 WSC (2ml/litre) or carbaryl 50 WP (0.1%, 4gms). · Apply copper oxychloride (0.25%) if fruit rot is observed. |
Common diseases
| Disease | Symptoms | Management |
| a). Fruit Rot | Dark or brown spots on fruits, leading to softening, watery decay, foul odor, andpremature fruit drop. Visible fungal growth or spores may appear in advanced stages. | Spray with captan (0.2%), Bordeaux mixture (1.0%), or copper oxychloride (0.25%) at three-week intervals during January, February, and March. |
| b). Dieback | Drying and browning of twig tips, wilting and yellowing of leaves, dark sunken cankers on branches, stunted growth, and gradual decline of the tree. | Prune and remove infected twigs. Spray with Carbendazim (0.1%), Thiophenate methyl (0.2%), or Chlorothalonil (0.2%). |
| c). Phytophthora Fruit Rot | Water-soaked, dark, and soft spots on fruits, rapid decay into mushy, discolored areas, white cottony fungal growth in humid conditions, and premature fruit drop with a foul smell. | Spray with Benomyl (1g/liter) to control the disease. |
| d). Leaf Spot | Small, circular, or irregular dark brown or black spots on leaves, often with yellow halos, leading to leaf yellowing, premature leaf drop, and reduced photosynthesis. | Spray with Carbendazim (0.1%), Thiophanate methyl (0.2%), or Difolatan (0.2%). Maintain orchard hygiene and remove infected leaves. |
Harvesting
It takes three to four years for jackfruit to ripen and yield edible fruits. Harvest the fruit when it smells good and makes a hollow sound when you tap it. To prolong shelf life and avoid damaging the tree, cut the fruit with a sharp knife, leaving a tiny stem intact. To prevent bruising, which can lead to spoiling and lower market value, handle with caution. Freshness and quality are guaranteed by appropriate harvesting and treatment.
Total Investment for 1 acre of Jackfruit Farming
To analyze the profitability of jackfruit farming per acre based on the provided information, we will calculate the total costs, total income, and net profit over the lifespan of the jackfruit orchard. We will also consider the annual maintenance costs and the income generated from the 3rd year onwards.
Initial Investment (First Year)
| Categories | Estimated Cost (NRs.) |
| Land Preparation | 40,000 |
| Jackfruit Saplings (63 plants * NRs. 300) | 18,900 |
| Fertilizers and Manure | 40,000 |
| Irrigation System (Drip) | 100,000 |
| Labor Costs (Planting, Maintenance) | 40,000 |
| Pest & Disease Control | 30,000 |
| Miscellaneous Costs | 30,000 |
| Total Initial Investment | 298,900 |
Annual maintenance Cost of Jackfruit Farming
In order to maintain the health and production of the orchard, the yearly maintenance cost for jackfruit farming is an essential part of the total investment. After the initial setup (land preparation, planting, and irrigation installation) is over, these expenses start to be spent in the second year. Depending on personnel, fertilizers, pest control, irrigation maintenance, and other incidentals, the annual maintenance costs usually fall between NRs. 50,000 and NRs. 100,000 per acre.
An average yearly maintenance cost of NRs. 75,000 per acre has been considered for the sake of this analysis. Routine tasks including fertilization, trimming, weeding, irrigation management, and disease and insect control are included in this number. For the jackfruit trees to develop healthily and provide their maximum potential yield, proper upkeep is necessary. Ignoring these tasks can result in lower output and more expenses down the road.
The annual maintenance cost remains relatively consistent throughout the lifespan of the orchard, from the second year until the end of its productive life (around 20–30 years). While it represents an ongoing expense, it is a necessary investment to maximize yields and ensure the long-term profitability of jackfruit farming. By maintaining the orchard properly, farmers can achieve higher fruit quality and quantity, ultimately leading to better market prices and increased income.
Income from 1 acre of Jackfruit Farming
Income from Jackfruit Farming
| Year | Yield per Tree (kg) | Yield per Acre (kg) | Market Price (NRs/kg) | Total Income (NRs.) |
| 3rd Year | 10 | 630 | 60 | 37,800 |
| 4th Year | 20 | 1,260 | 60 | 75,600 |
| 5th Year | 40 | 2,520 | 70 | 176,400 |
| 6th Year | 60 | 3,780 | 80 | 302,400 |
| 7th–20th Year | 90 | 5,670 | 100 | 567,000 |
| 21st Year+ | 60 | 3,780 | 120 | 453,600 |
Analysis of Jackfruit Farming Profit per Acre
Jackfruit farming requires a significant initial investment and a long waiting period before it becomes profitable. In the first six years, farmers incur losses due to high setup costs, including land preparation, saplings, irrigation, and labor, along with low or no income from the trees. Cumulative loss peaks in the third year at NRs. -411,100, and the break-even point is only achieved in the seventh year when the orchard starts generating steady income.
From the seventh year onwards, jackfruit farming becomes highly profitable. With an annual income of NRs. 567,000 and maintenance costs of NRs. 75,000 farmers can expect a net profit of NRs. 492,000 per year. This phase, lasting from Year 7 to Year 20, is the most rewarding, as the trees reach full production and generate consistent yields.
By the end of the 20-year lifespan, the cumulative profit from jackfruit farming can reach NRs. 6,806,300 per acre. While the initial years require patience and investment, long-term profitability makes jackfruit farming a sustainable and lucrative venture for farmers willing to manage the costs and wait for the trees to mature.


